Joins & Junctions in Workflows
Bring branches of workflow together using Joins & Junctions
Overview
Joins and Junctions are extremely useful but are also frequently misunderstood. Both tasks are System Utilites and serve a similar purpose: to bring together processing of multiple branches of a workflow. The usage scenarios for each are very different and largely dependant on how your workflow is designed and what business rules and processes you need to support.
Basic Workflow Engine Overview
Here are a few basic concepts of the workflow engine. If you are already familiar with basic concepts feel free to skip to the next section.
- Workflow is processed by the Task Engine in the form of a Task Tree or Routine.
- Each workflow represents a process, by modeling it with a tree or branching structure.
- Workflows consist of nodes and connectors.
- A node represents an independent piece of code that processes data.
- A connector links the nodes together and allows for logic and qualifications to determine processing.
When the task engine is asked to process a workflow, it follows the path(s) of connectors and processes nodes.
Join and Junction Overview
With a basic understanding of workflow processing, now we can talk about Joins and Junction. Even a simple workflow can include multiple branches. Joins and Junctions let you bring the process back to a single branch. You also have the option to determine when that branch progresses.
Here is an example where a join and junction are not required:

Even though the workflow contains a deferred node (order product) and a branch to three nodes, it doesn't need a join or junction to bring branches back together.
Here's an example of a workflow that does need a join or junction:
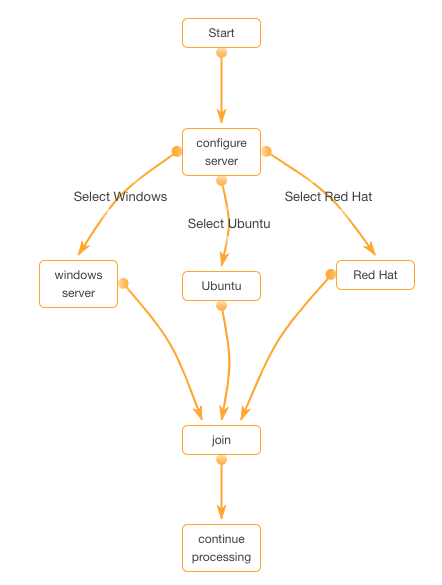
In this workflow you can see that three tasks process at the same time, but only one operating system should be installed on the server. The join node needs to restrict processing based on rules (one operating system per server).
Join
A Join node deals directly with the connectors that lead into it. As soon as the first connector reaches the Join, the Task Engine calculates whether it should complete the Join node and continue the tree, or if it needs to wait for more connectors. The property that determines if the Task engine waits or not is the Type setting on the Join.

These are the options for Type:
- All. Every connector leading into the join must process before the join completes and then processing continues farther down the workflow.
- Any. As soon as one connector leading into the Join processes, the Join node completes and processing continues down the workflow.
- Some. When you select Some, you must also add a number to signify how many connectors it takes to process before the Join node completes and the process continues
Here is an example of the three connectors and an Any Join:

As soon as any one of the connectors make it to the Join node, it will complete and continue processing.
Junction
The difference between a Join and Junction is how far back up the workflow each utility looks to determine if it should be complete. A join only looks at the connectors that directly connect to it. A Junction looks back at each branch that connects to it, back to a common parent.
Here is a basic example:

As you can see from the screenshot, a Junction node has no parameters to set. It relies entirely on evaluating the branches that lead into it.
In this case, all the branches that eventually lead to the Junction node start at the "select new employee software node". The branch on the far right completes automatically (no qualifications on the connetor and not a deferred node), but the junction will still evaluate the other branches to see if they are as complete as possible.
Complete as possible means that the Task Engine is not waiting for a deferred node to be complete and all connector qualifications on the branch (that can be evaluated) are evaluated.
In the above example, if the connector qualifications for all three branches that have them fail (evaluate to false), the Junction node considers those branches complete and continues processing down the tree. Note that the paths to not have to successfully reach the Junction by evaluating to true.
It can also be the case that the Junction will wait for a deferred node for as long as it takes. Be cautious on what processes you place on the branches leading to a junction.
Updated 3 months ago
